Life Expectancy By Country
Last updated February 28, 2026
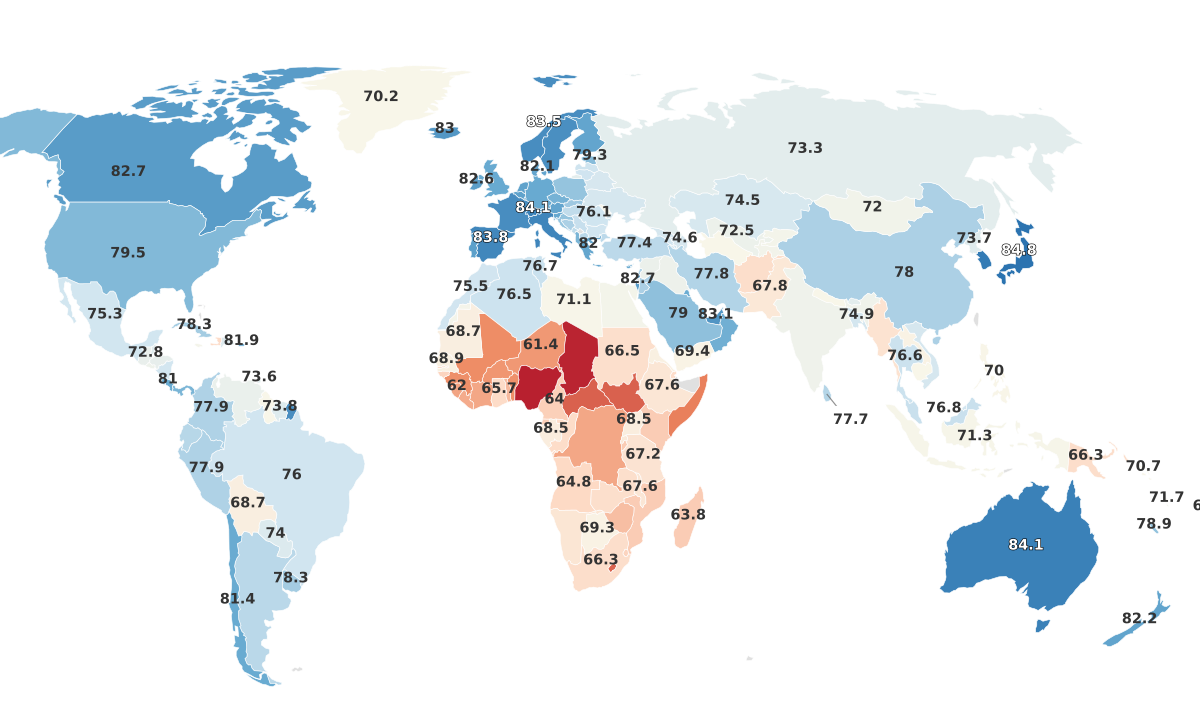
Life Expectancy Globally
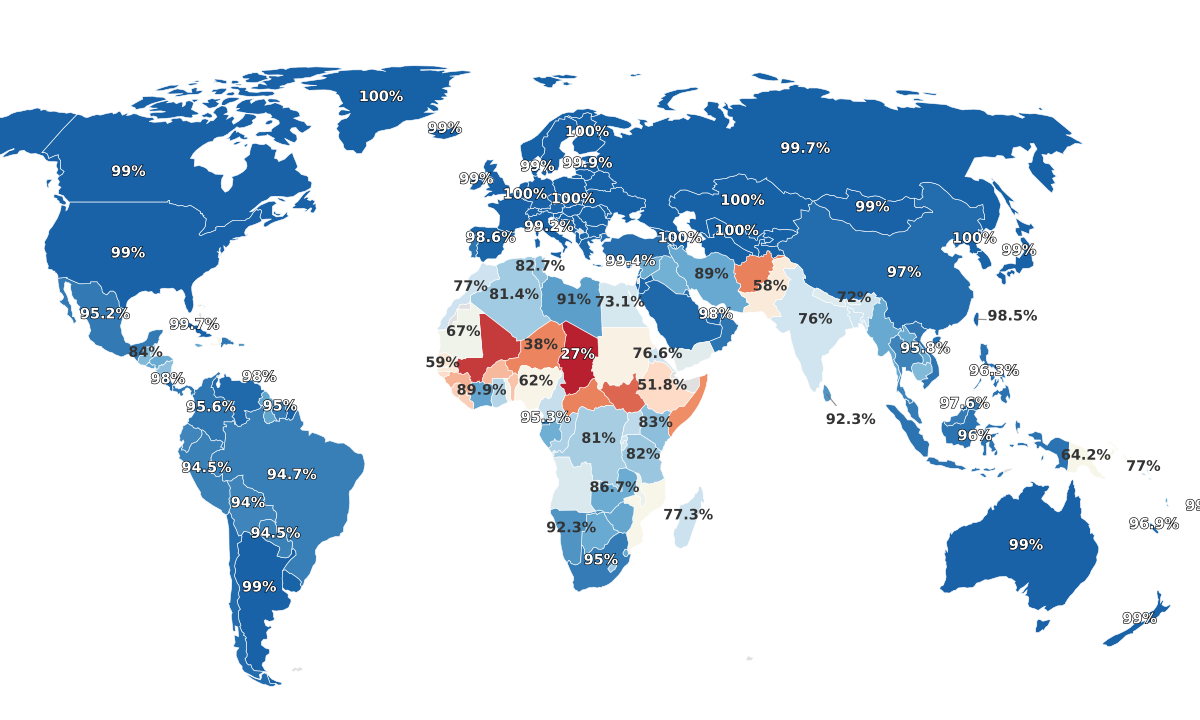
The measure of 'life expectancy' not only indicates the average age a person is expected to live but offers a crucial insight into the overall health and living standards of a country. It is influenced by a variety of factors including healthcare accessibility, nutritional standards, living conditions, and socio-economic factors. The World Health Organization and other international bodies regularly compile, analyze, and publish data on life expectancy to monitor global health trends. Interestingly, as per the data, the United States ranks relatively low in the list of countries by life expectancy, coming in at 58th place with a life expectancy of 79.74 years, despite being one of the world's most developed nations. A myriad of factors including healthcare costs, obesity rates, and socioeconomic disparities contribute to this ranking. Key findings from the data include:
- Monaco leads the world with the highest life expectancy at 87.01 years, closely followed by Hong Kong (85.83 years) and Macau (85.51 years). This can be attributed to their high-quality healthcare, affluent lifestyles, and low levels of pollution.
- In contrast, Chad has the lowest life expectancy at a mere 53.68 years due to ongoing conflict, high levels of poverty, and limited access to quality healthcare.
- Many high-income countries such as Japan (84.95 years), Switzerland (84.38 years), and Singapore (84.27 years) feature in the top ten countries for life expectancy, underscoring the correlation between wealth and long lifespan.
- However, it's noteworthy that a high GDP does not necessarily guarantee a long life span, as seen in the case of the United States.
- Disparities between lower and higher-income countries remain stark, with a difference of 33.33 years between the nations with the highest and lowest life expectancies. This unique lens of life expectancy provides an avenue to explore the effects of countries' public health policies, socio-economic conditions, and lifestyle choices while pointing out critical areas for potential improvement. The journey towards equitable global health is ongoing, and these insights prove valuable in informing and shaping that trajectory.
All Metrics
| Region ↕ | Life Expectancy 2024↕ | Female Life Expectancy 2024↕ | Male Life Expectancy 2024↕ | Bloomberg Global Health Index↕ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monaco | 86.5 | 88.6 | 84.6 | |
| San Marino | 85.8 | 87.2 | 84.3 | |
| Hong Kong | 85.6 | 88.3 | 83 | |
| Japan | 84.8 | 87.9 | 81.8 | 91.38 |
| South Korea | 84.4 | 87.3 | 81.3 | 85.41 |
| Saint Barthelemy | 84.4 | 86.9 | 81.6 | |
| Andorra | 84.2 | 86.2 | 82.3 | |
| French Polynesia | 84.2 | 86.6 | 81.9 | |
| Switzerland | 84.1 | 86 | 82.2 | 90.93 |
| Australia | 84.1 | 85.5 | 82.3 | 89.75 |
| Singapore | 83.9 | 86.4 | 81.4 | 89.29 |
| Italy | 83.9 | 85.9 | 81.8 | 91.59 |
| Spain | 83.8 | 86.4 | 81.1 | 92.75 |
| Liechtenstein | 83.8 | 85.4 | 82 | |
| Reunion | 83.7 | 86.5 | 80.7 | |
| Gibraltar | 83.6 | 86.2 | 81 | |
| Malta | 83.5 | 85.4 | 81.5 | 81.70 |
| Norway | 83.5 | 85 | 81.9 | 89.09 |
| France | 83.5 | 86.2 | 80.6 | 86.94 |
| Sweden | 83.4 | 85.2 | 81.7 | 90.24 |
| Macau | 83.2 | 85.3 | 81 | |
| Vatican City | 83.1 | 85.2 | 81 | |
| United Arab Emirates | 83.1 | 84.3 | 82.2 | 67.14 |
| Iceland | 83 | 84.5 | 81.6 | 91.44 |
| Canada | 82.7 | 84.9 | 80.5 | |
| Martinique | 82.7 | 85.7 | 79.5 | |
| Israel | 82.7 | 84.7 | 80.7 | 88.15 |
| Ireland | 82.6 | 84.6 | 80.6 | 84.06 |
| Portugal | 82.5 | 85.3 | 79.7 | 83.10 |
| Bermuda | 82.5 | 85.9 | 79.1 | |
| Qatar | 82.5 | 83.5 | 81.8 | 71.97 |
| Luxembourg | 82.4 | 83.9 | 80.8 | 87.39 |
| Belgium | 82.3 | 84.5 | 80.1 | 80.46 |
| Netherlands | 82.3 | 83.8 | 80.7 | 85.86 |
| New Zealand | 82.2 | 83.9 | 80.6 | |
| Guadeloupe | 82.2 | 85.7 | 78.3 | |
| Denmark | 82.1 | 84 | 80.2 | 82.69 |
| Austria | 82.1 | 84.5 | 79.8 | 86.30 |
| Finland | 82.1 | 84.8 | 79.4 | 85.89 |
| Greece | 82 | 84.5 | 79.5 | 82.29 |
| Puerto Rico | 81.9 | 85.4 | 78.3 | |
| Slovenia | 81.8 | 84.5 | 79.1 | 82.72 |
| Cyprus | 81.8 | 83.8 | 79.8 | 83.58 |
| United Kingdom | 81.5 | 83.3 | 79.5 | 84.28 |
| Germany | 81.5 | 83.9 | 79.2 | 83.06 |
| Chile | 81.4 | 83.2 | 79.5 | 73.21 |
| Bahrain | 81.4 | 82.1 | 80.8 | 72.31 |
| Maldives | 81.3 | 83 | 80 | 70.95 |
| Isle Of Man | 81.1 | 83.2 | 79 | |
| Costa Rica | 81 | 83.6 | 78.4 | 73.21 |
| Kuwait | 80.6 | 82 | 79.5 | |
| Cayman Islands | 80.5 | 83 | 78.2 | |
| Saint Martin | 80.4 | 84 | 77 | |
| Oman | 80.3 | 82 | 78.7 | 64.07 |
| Czech Republic | 80 | 82.8 | 77.2 | 77.59 |
| Panama | 79.8 | 82.7 | 76.9 | 64.01 |
| Albania | 79.8 | 81.6 | 77.9 | 68.04 |
| Anguilla | 79.5 | 82.8 | 76.2 | |
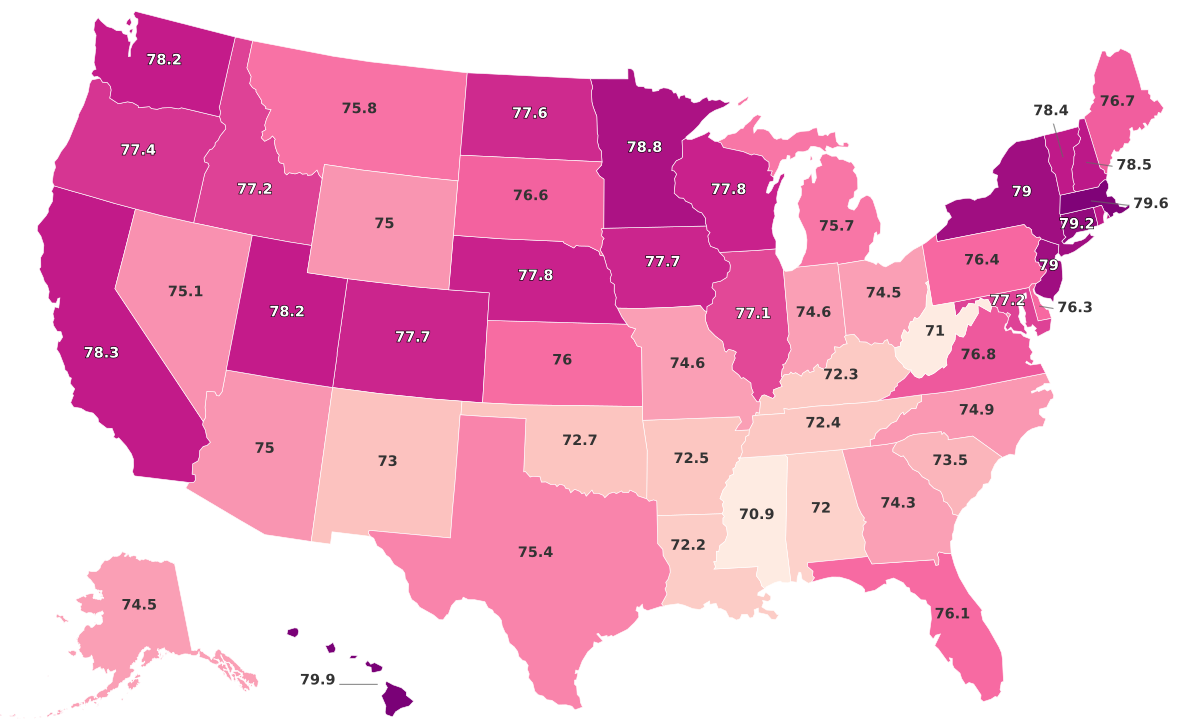
| United States | 79.5 | 82 | 77 | 73.02 |
| Estonia | 79.3 | 83.2 | 75.1 | 73.32 |
| Northern Mariana Islands | 79 | 80.9 | 77.3 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 79 | 81.3 | 77.3 | |
| New Caledonia | 78.9 | 81.4 | 76.5 | |
| Croatia | 78.8 | 81.8 | 75.6 | 73.36 |
| Poland | 78.8 | 82.5 | 75.1 | 70.25 |
| Slovakia | 78.5 | 81.7 | 75.2 | |
| Uruguay | 78.3 | 82 | 74.4 | 65.66 |
| Cuba | 78.3 | 80.7 | 75.9 | 74.66 |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | 78.2 | 80.5 | 76 | |
| Lebanon | 78 | 79.9 | 75.9 | 70.53 |
| China | 78 | 81 | 75.3 | 62.52 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 78 | 81.1 | 74.7 | 69.66 |
| Jordan | 78 | 80.3 | 75.9 | |
| Peru | 77.9 | 80.3 | 75.6 | |
| Colombia | 77.9 | 80.6 | 75.2 | |
| Iran | 77.8 | 79.8 | 76 | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | 77.8 | 80.5 | 74.7 | |
| Sri Lanka | 77.7 | 80.8 | 74.5 | |
| Ecuador | 77.6 | 80.3 | 74.9 | |
| Argentina | 77.5 | 80 | 75 | 61.19 |
| North Macedonia | 77.5 | 79.7 | 75.3 | |
| British Virgin Islands | 77.4 | 80.2 | 74.7 | |
| Turkey | 77.4 | 80.3 | 74.6 | 62.81 |
| Guam | 77.4 | 81.6 | 73.7 | |
| Montenegro | 77.3 | 80.5 | 73.9 | 69.69 |
| French Guiana | 77.2 | 80.2 | 74.3 | |
| Hungary | 77.2 | 80.3 | 73.9 | 64.43 |
| Curacao | 77 | 81 | 72.7 | |
| Saint Pierre and Miquelon | 76.9 | 81.6 | 73 | |
| Serbia | 76.9 | 80.2 | 73.7 | 60.99 |
| Malaysia | 76.8 | 79.5 | 74.5 | |
| Tunisia | 76.7 | 79.3 | 74.1 | |
| Thailand | 76.6 | 81 | 72.3 | |
| Aruba | 76.5 | 78.9 | 73.8 | |
| Algeria | 76.5 | 77.9 | 75.1 | |
| Montserrat | 76.3 | 79 | 74.3 | |
| Latvia | 76.3 | 80.6 | 71.8 | |
| Barbados | 76.3 | 78.8 | 73.8 | |
| Mayotte | 76.2 | 78.5 | 74.3 | |
| Cape Verde | 76.2 | 79.4 | 73 | |
| Lithuania | 76.2 | 80.8 | 71.4 | |
| Romania | 76.1 | 79.7 | 72.6 | |
| Brazil | 76 | 79.2 | 73 | |
| Armenia | 75.8 | 79.6 | 71.6 | |
| Bulgaria | 75.8 | 79.4 | 72.3 | |
| Morocco | 75.5 | 77.8 | 73.3 | |
| Cook Islands | 75.5 | 79.2 | 72.1 | |
| Brunei | 75.5 | 77.7 | 73.5 | 67.96 |
| Grenada | 75.4 | 78.5 | 72.5 | |
| Mexico | 75.3 | 78 | 72.4 | 62.09 |
| Nicaragua | 75.1 | 77.6 | 72.5 | |
| Mauritius | 75.1 | 78.3 | 72.1 | |
| Bangladesh | 74.9 | 76.7 | 73.3 | |
| Bahamas | 74.7 | 78.3 | 71.1 | |
| Vietnam | 74.7 | 79.4 | 70 | |
| Ukraine | 74.7 | 79.4 | 69.8 | |
| Georgia | 74.7 | 79.2 | 69.8 | |
| Azerbaijan | 74.6 | 77.3 | 71.7 | |
| Belarus | 74.6 | 79.2 | 69.7 | |
| Kazakhstan | 74.5 | 78.5 | 70.3 | |
| Paraguay | 74 | 77.1 | 71 | |
| Dominican Republic | 73.9 | 77.1 | 70.7 | |
| Suriname | 73.8 | 77 | 70.6 | |
| North Korea | 73.7 | 75.9 | 71.5 | |
| Belize | 73.7 | 76.7 | 71.1 | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 73.6 | 76.8 | 70.5 | |
| Bhutan | 73.3 | 75.3 | 71.6 | |
| Russia | 73.3 | 79.2 | 67.5 | |
| Tonga | 73.1 | 76.5 | 69.5 | |
| Seychelles | 73 | 76.7 | 70.1 | |
| Honduras | 73 | 75.7 | 70.5 | |
| American Samoa | 73 | 76 | 70.3 | |
| Saint Lucia | 72.8 | 76.5 | 69.5 | |
| Guatemala | 72.8 | 75 | 70.4 | |
| Venezuela | 72.7 | 76.7 | 68.9 | |
| Syria | 72.6 | 74.9 | 70.2 | |
| Uzbekistan | 72.5 | 75.5 | 69.6 | |
| Iraq | 72.4 | 74.2 | 70.5 | |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 72.3 | 76.2 | 68.7 | |
| El Salvador | 72.3 | 76.5 | 67.8 | |
| India | 72.2 | 73.9 | 70.7 | |
| Mongolia | 72 | 76.7 | 67.5 | |
| Tajikistan | 71.9 | 74.1 | 69.7 | |
| Egypt | 71.8 | 74 | 69.7 | |
| Samoa | 71.8 | 73.8 | 70 | |
| Kyrgyzstan | 71.8 | 75.4 | 68.3 | |
| Vanuatu | 71.7 | 74.1 | 69.6 | |
| Western Sahara | 71.6 | 73.8 | 69.9 | |
| Jamaica | 71.6 | 74.2 | 69.1 | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 71.4 | 74.5 | 68.8 | |
| Moldova | 71.3 | 75.7 | 66.7 | |
| Indonesia | 71.3 | 73.4 | 69.2 | |
| Dominica | 71.3 | 74.7 | 68.3 | |
| Libya | 71.1 | 72.7 | 69.6 | |
| Cambodia | 70.8 | 73.4 | 68.2 | |
| Solomon Islands | 70.7 | 72.2 | 69.4 | |
| Nepal | 70.6 | 72.1 | 69.1 | |
| Guyana | 70.3 | 74.1 | 66.6 | |
| Turkmenistan | 70.2 | 73 | 67 | |
| Greenland | 70.2 | 72.6 | 68.2 | |
| Niue | 70.1 | 72.9 | 67.5 | |
| Philippines | 70 | 73 | 67 | |
| Sao Tome and Principe | 69.9 | 73.9 | 66.4 | |
| Yemen | 69.4 | 71.5 | 67.4 | |
| Palau | 69.4 | 71.9 | 67.3 | |
| Botswana | 69.3 | 71.8 | 66.8 | |
| Laos | 69.2 | 71.5 | 67 | |
| Palestine | 69.2 | 74.3 | 65.2 | |
| Senegal | 68.9 | 71 | 67 | |
| Eritrea | 68.9 | 70.9 | 66.8 | |
| Mauritania | 68.7 | 70.7 | 66.7 | |
| Bolivia | 68.7 | 71.3 | 66.3 | |
| Uganda | 68.5 | 71.4 | 65.5 | |
| Gabon | 68.5 | 71.2 | 66.1 | |
| Rwanda | 68 | 70.1 | 65.7 | |
| Timor Leste | 67.9 | 69.7 | 66.3 | |
| Pakistan | 67.8 | 70.3 | 65.5 | |
| Malawi | 67.6 | 70.8 | 64.3 | |
| Ethiopia | 67.6 | 71 | 64.3 | |
| Fiji | 67.5 | 69.5 | 65.5 | |
| Namibia | 67.5 | 71.5 | 63.5 | |
| Micronesia | 67.4 | 71.3 | 63.6 | |
| Tuvalu | 67.3 | 70.9 | 63.9 | |
| Tanzania | 67.2 | 70 | 64.4 | |
| Marshall Islands | 67.1 | 69.5 | 65 | |
| Myanmar | 67.1 | 70.4 | 64 | |
| Comoros | 67 | 69.2 | 65 | |
| Kiribati | 66.6 | 68.3 | 64.7 | |
| Zambia | 66.5 | 68.9 | 64.1 | |
| Sudan | 66.5 | 69.8 | 63.5 | |
| Afghanistan | 66.3 | 67.8 | 64.7 | |
| South Africa | 66.3 | 69.8 | 62.8 | |
| Papua New Guinea | 66.3 | 69.2 | 63.8 | |
| Djibouti | 66.2 | 68.7 | 63.7 | |
| Gambia | 66.1 | 67.8 | 64.3 | |
| Republic of the Congo | 66 | 67.7 | 64.3 | |
| Ghana | 65.7 | 68.2 | 63.3 | |
| Haiti | 65.1 | 68.5 | 61.9 | |
| Angola | 64.8 | 67.3 | 62.3 | |
| Eswatini | 64.3 | 67.1 | 61.3 | |
| Guinea Bissau | 64.3 | 66.5 | 61.8 | |
| Cameroon | 64 | 66.2 | 61.8 | 85.70 |
| Equatorial Guinea | 63.9 | 65.9 | 62.2 | |
| Mozambique | 63.8 | 66.7 | 60.5 | |
| Madagascar | 63.8 | 65.6 | 62.1 | |
| Kenya | 63.8 | 66.1 | 61.6 | |
| Burundi | 63.8 | 65.9 | 61.8 | |
| Zimbabwe | 63.1 | 65.3 | 60.5 | |
| Togo | 62.9 | 63.1 | 62.7 | |
| Liberia | 62.3 | 63.6 | 61 | |
| Nauru | 62.3 | 64.2 | 60.4 | |
| DR Congo | 62.1 | 64.2 | 60 | |
| Ivory Coast | 62.1 | 64.3 | 60.2 | |
| Sierra Leone | 62 | 63.7 | 60.2 | |
| Niger | 61.4 | 62.4 | 60.5 | |
| Burkina Faso | 61.3 | 63.4 | 59.1 | |
| Benin | 61 | 62.4 | 59.5 | |
| Guinea | 60.9 | 62.1 | 59.7 | |
| Mali | 60.7 | 62.1 | 59.3 | |
| Somalia | 59 | 61.5 | 56.5 | |
| Lesotho | 57.8 | 60.4 | 55 | |
| Central African Republic | 57.7 | 59.6 | 55.5 | |
| South Sudan | 57.7 | 60.8 | 54.8 | |
| Chad | 55.2 | 57.2 | 53.4 | |
| Nigeria | 54.6 | 54.9 | 54.3 |
Countries With Highest Life Expectancy
Among the world's countries, Monaco, Hong Kong, Macau, Japan, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Singapore, Italy, Vatican City, and South Korea come out on top in terms of life expectancy. Topping off the list is Monaco with an impressive average life expectancy of 87.01 years. Following closely in second place is Hong Kong, with citizens expected to live an average of 85.83 years. Macau comes in third place with an impressive average life expectancy of 85.51 years, closely followed by Japan with 84.95 years. Next on the list is Liechtenstein with an average life expectancy of 84.77 years, Switzerland with 84.38 years, Singapore with 84.27 years, and Italy with 84.20 years. The Vatican City also demonstrates high life expectancy figures with an average of 84.16 years. Lastly, South Korea rounds up the top ten with an average life expectancy of 84.14 years. 10 Countries with Highest Life Expectancy:
- Monaco - 87.01 years
- Hong Kong - 85.83 years
- Macau - 85.51 years
- Japan - 84.95 years
- Liechtenstein - 84.77 years
- Switzerland - 84.38 years
- Singapore - 84.27 years
- Italy - 84.20 years
- Vatican City - 84.16 years
- South Korea - 84.14 years
Countries With Lowest Life Expectancies
The countries with the lowest life expectancies span the continents of Africa with Chad, Nigeria, Lesotho, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Somalia, Eswatini (Swaziland), Namibia, Guinea, and Mali rounding off the bottom ten. Chad has the lowest life expectancy of all, with an average of just 53.68 years. Close behind is Nigeria with a life expectancy of 53.87 years. The small country of Lesotho, surrounded by South Africa, reports a life expectancy of 54.91 years. Central African Republic has a life expectancy of 55.48 years, while South Sudan reports an average life expectancy of 56.51 years. Other countries in this list include Somalia, with an average life expectancy of 57.35 years and Eswatini (Swaziland) with a life expectancy of 57.71 years. Namibia and Guinea have slightly higher life expectancies of 59.53 and 59.55 years respectively, with Mali rounding off this list with a life expectancy of 60.03 years. 10 Countries With Lowest Life Expectancies:
- Chad - 53.68 years
- Nigeria - 53.87 years
- Lesotho - 54.91 years
- Central African Republic - 55.48 years
- South Sudan - 56.51 years
- Somalia - 57.35 years
- Eswatini (Swaziland) - 57.71 years
- Namibia - 59.53 years
- Guinea - 59.55 years
- Mali - 60.03 years While many factors can contribute to these low life expectancies, pervasive issues typically include poor access to quality healthcare, social instability, malnutrition, and high prevalence of diseases.
Sources & Notes
Average number of years a newborn is expected to live.
Average number of years a woman is expected to live.
Average number of years a man is expected to live.